Learn the secrets to the best possible brain health by exploring the relationship between neuronal function, exercise, and lifestyle. Examine the complex interactions between these elements to improve lifespan & cognitive health. We light the route to a sharper mind with anything from the most recent research discoveries to useful recommendations. Come along for this journey with us to discover your brain’s full potential and adopt a healthy way of living.
How Lifestyle & Exercise Affects the Brain
Fitness & lifestyle choices have a tremendous effect on the brain, influencing psychological well-being and cognitive performance. Frequent physical exercise promotes the creation of fresh neuron & improves brain connection by releasing neurotransmitters and growth factors. Exercise also encourages greater blood flow to the brain, which removes toxins and supplies vital minerals and oxygen. Throughout the meanwhile, lifestyle decisions like nutrition, sleep habits, and stress reduction are critical to maintaining brain health since they affect both neuronal function and cognitive function. People may improve the functioning of their minds, encourage neuroplasticity, and avoid dementia by adopting a balanced lifestyle and taking part in regular exercise.
What Is a Neuron?
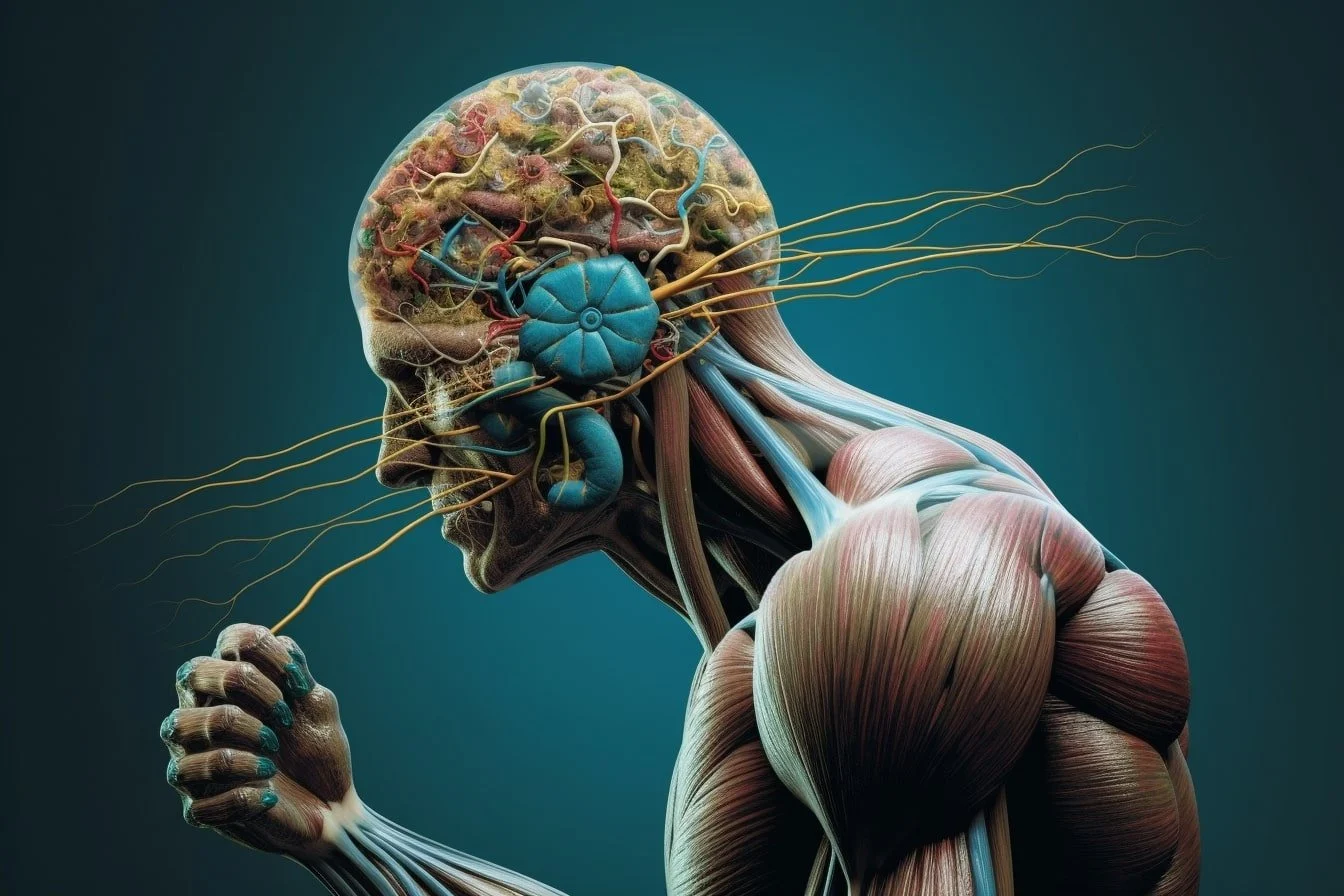
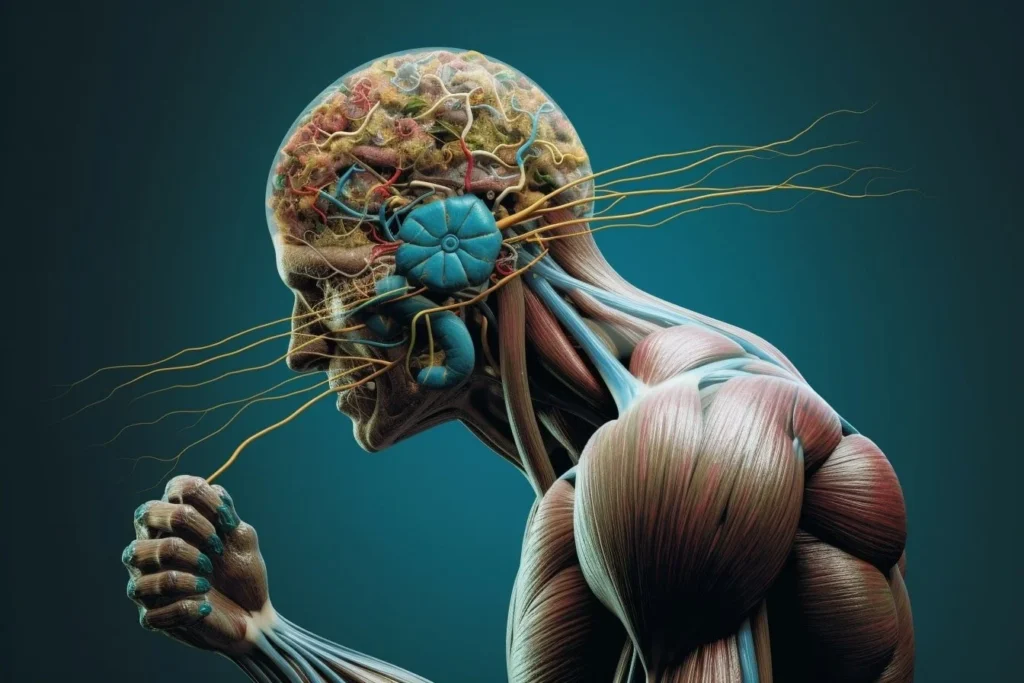
As the essential unit of the nervous system and a means for interaction between various body components, a neuron is a specialized cell. The axon, dendrites, plus cell body (soma) make up the structural components of neurons. It sends energy, or action potentials, to different neurons, muscles, and glands, while the dendrites receive messages from other neurons or sense receptors. Neurotransmitters are produced to transfer messages at the synapses, or junctions, between neurons. Neural networks, which support a variety of physiological processes, sensory perceptions, and cognitive activities, are intricately formed by neurons, which are essential for the processing and transmission of information throughout the body.
What Is the Hippocampus
The hippocampus region, found in the medial temporal lobe of the brain, is home to the tiny, seahorse-shaped structure known as the hippocampus. It is an essential part of the limbic system, which is charge with memory, emotion, and spatial orientation.
In a process known as recall, it is essential for transforming short-term memories into long-term ones. Also, the hippocampus plays a role in spatial memory and navigation, assisting people with orientation in their surroundings and space navigation.
Strong memory deficits, including both anterior amnesia—the inability to acquire new memories—and spatial disorientation, can result from damage or malfunction to the hippocampal.
The Link Between Exercise and Brain
There is a unique bond between exercise and the brain. Your body releases feel-good & stress-relieving compounds termed endorphins during exercise. But that’s not all there is to it! Engaging in physical activity also stimulates the growth of fresh neurons, which enhances cognitive function and memory. It maintains the brain’s functioning properly and enhances its performance through boosting the flow of nutrients and oxygen to it. Thus, regular activity helps you stay physically strong as well as mentally alert and concentrated.
What Happens to Our Brain When We Don’t Exercise
We lose from major advantages for the brain when we don’t exercise. It receives less blood flow when it is not physically active, which restricts the amount of oxygen and other nutrients it may get. Furthermore, there is a possible decrease in the synthesis of chemicals that improve mood, such as endorphins, which may result in feelings of tension, worry, and despair. Essentially, skipping exercise causes the brain to get inadequate nutrition and stimulation, which impairs the brain’s general health and functionality.